Method 1: Using Task Manager
The Windows Task Manager can help you in checking GPU health.
Step 1: Select the Performance tab, and select GPU in the left-side panel. If you’ve got more than one GPU, choose the one in use.
The idle one won’t show any real-time data. On the contrary, the active GPU will show live charts and graphs. This is how you can determine which one is the active GPU.

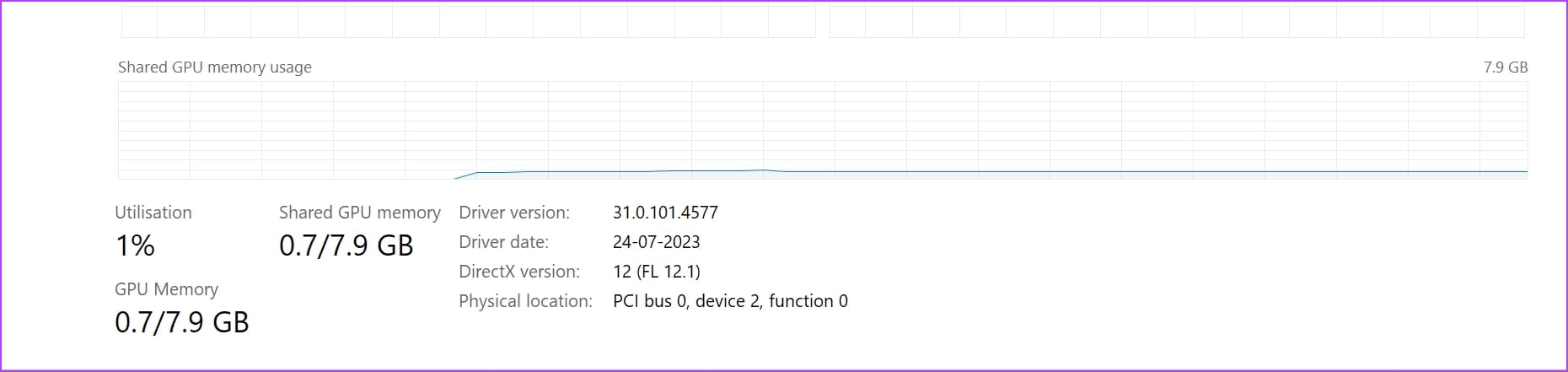
Step 2: Focus on the following data parameters on a live chart of an active GPU –
- The tool appropriately shows the Driver version, Driver date, DirectX version, and Physical location. When data for the above parameters are missing or incorrect, this indicates a faulty GPU.
- You may also be able to check the GPU Temperature. GPU Temperature stays within the room temperature or a few degrees above or below the room temperature in the resting state. It’s the state when you’re not running any game or graphic designing tool that uses the GPU.
- If the GPU temperature is 20°C to 25°C more than the room temperature in the resting state, the GPU health check indicates that the GPU cooling fan might be faulty.
Method 2: Using DXDIAG Command
DXDIAG is the short form for DirectX Diagnostic Tool. It comes out of the box with Windows operating systems like Windows 7, Windows 10, Windows 11, etc. This will work only if you’re using a DirectX-enabled GPU.
Step 1: Press Windows + R together. The Run tool will open.
Step 2: Type dxdiag and hit Enter.
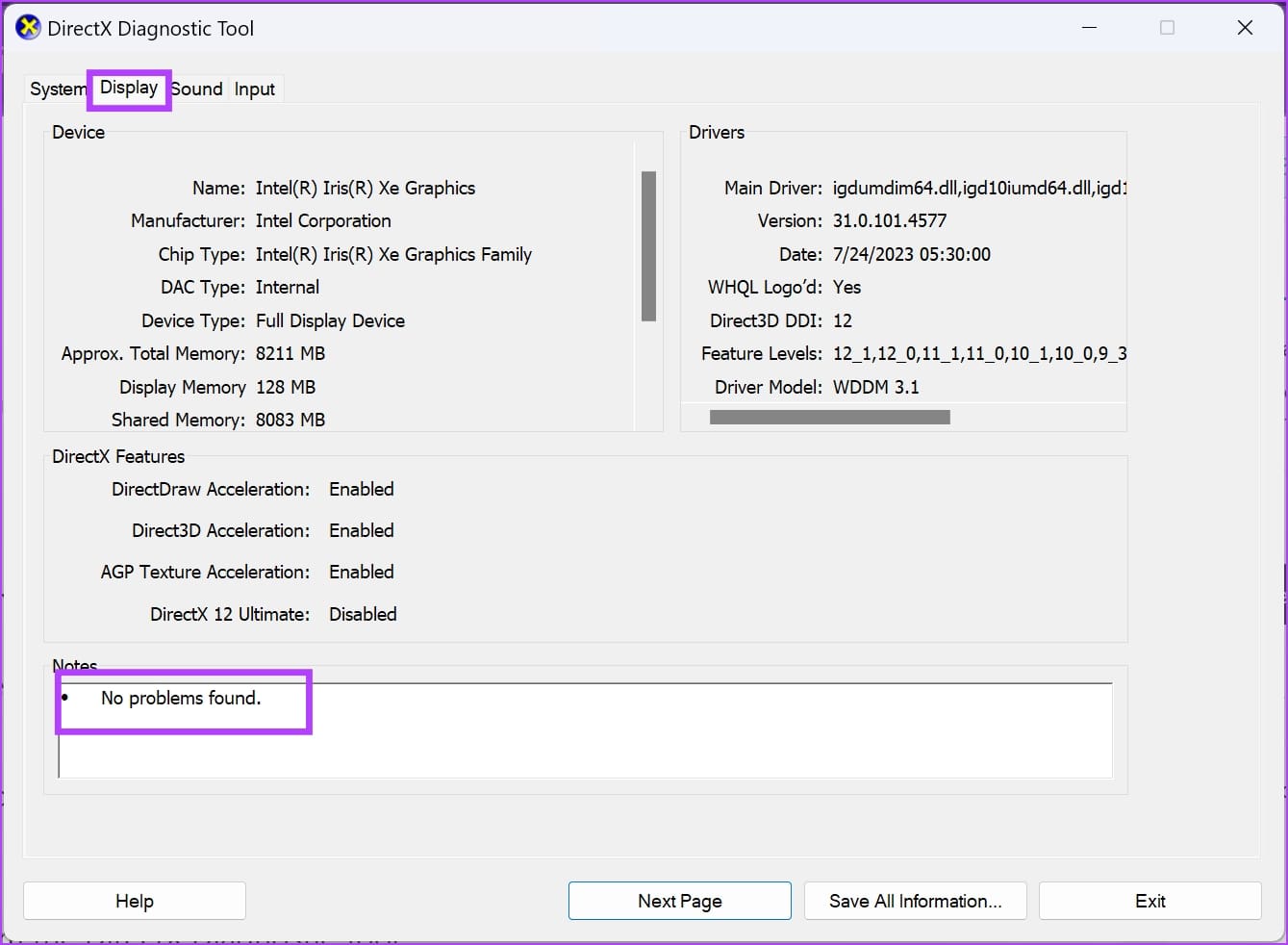
Here’s how to gauge the GPU health from the DirectX Diagnostic Tool:
- Read the information in the Device section. Match the data with the specifications of the GPU supplied in the manufacturer’s manual.
- Review the active features in the DirectX Features section. DirectDraw, Direct3D, and AGP Texture Acceleration should show Enabled. If these properties are empty or the tool shows Not Available, there’s a problem with the GPU driver or hardware.
Method 3: Use Windows Settings
You can also find out if the GPU health is good or not from the Windows Settings tool. Here’s how:
Step 1: Press Windows + I to open Windows Settings.
Step 2: Select System and then click Display.
Step 3: Scroll down to find Advanced display settings on the right-side panel. Click on it.
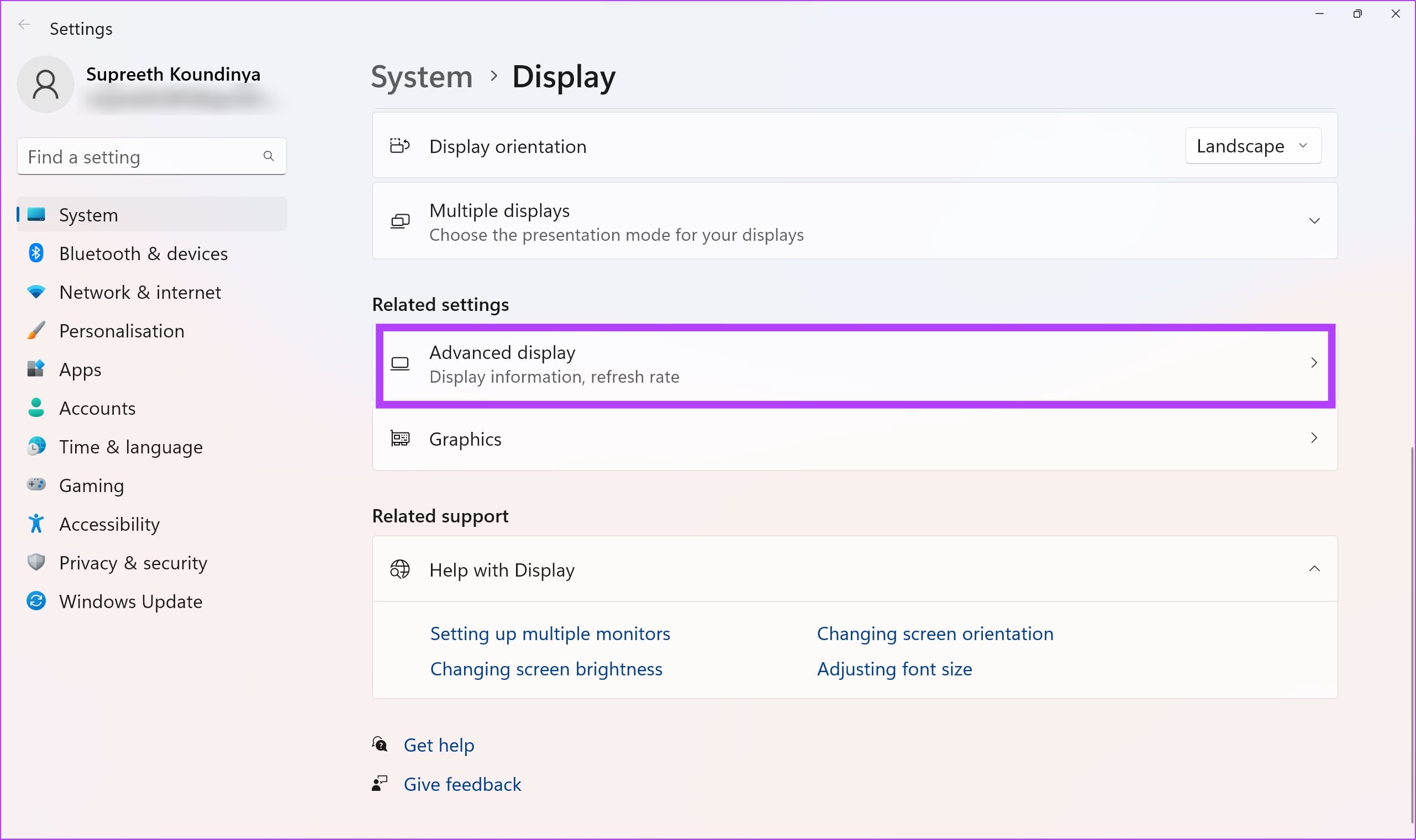
Step 4: Now, select Display adapter properties.
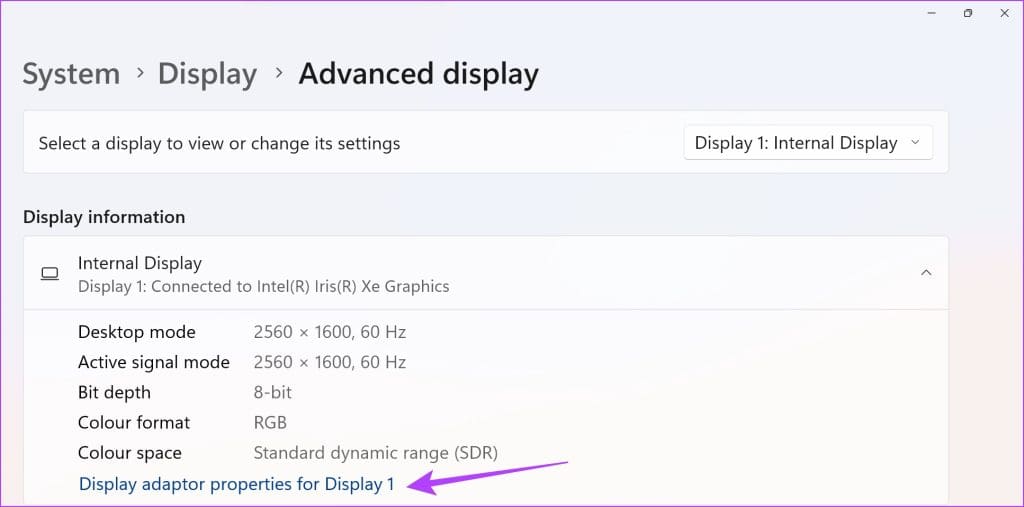
Step 5: Click on Properties.
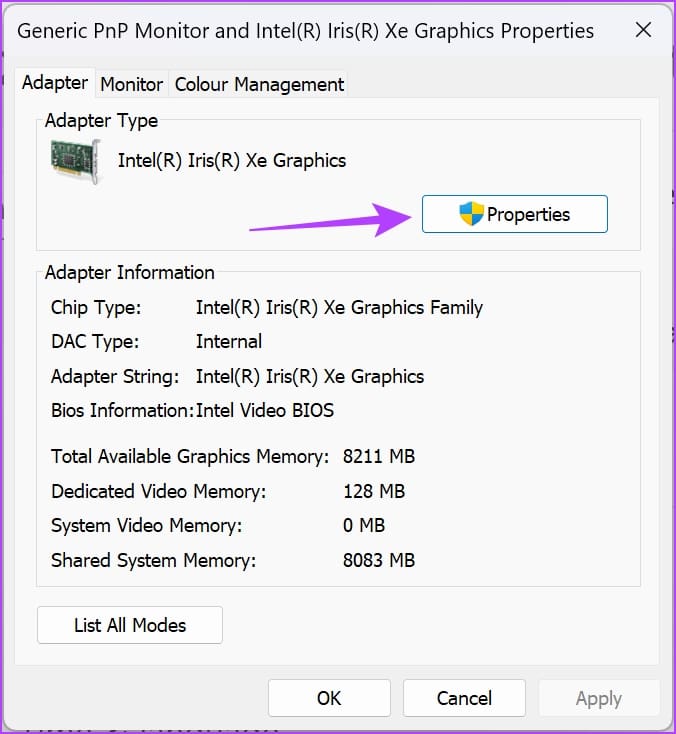
Step 5: Check the Device status message.
If the Device status text shows “This device is working properly,” then the GPU is in good health. However, if the status shows any warning or error codes, then the GPU must be suffering from hardware or software faults.
So far, the above GPU health check methods give you a qualitative health status of the GPU. To know actual figures, you can use a benchmarking tool as mentioned below.
Method 4: Using a GPU Diagnostics Tool
You can get the Geeks3D FurMark GPU benchmarking tool to find advanced data on your GPU health. The tool is free for download from the official website of Geeks3D.
Download the app and install it. Once you’ve installed the tool, follow these steps:
Step 1: Run the app from the Start menu.
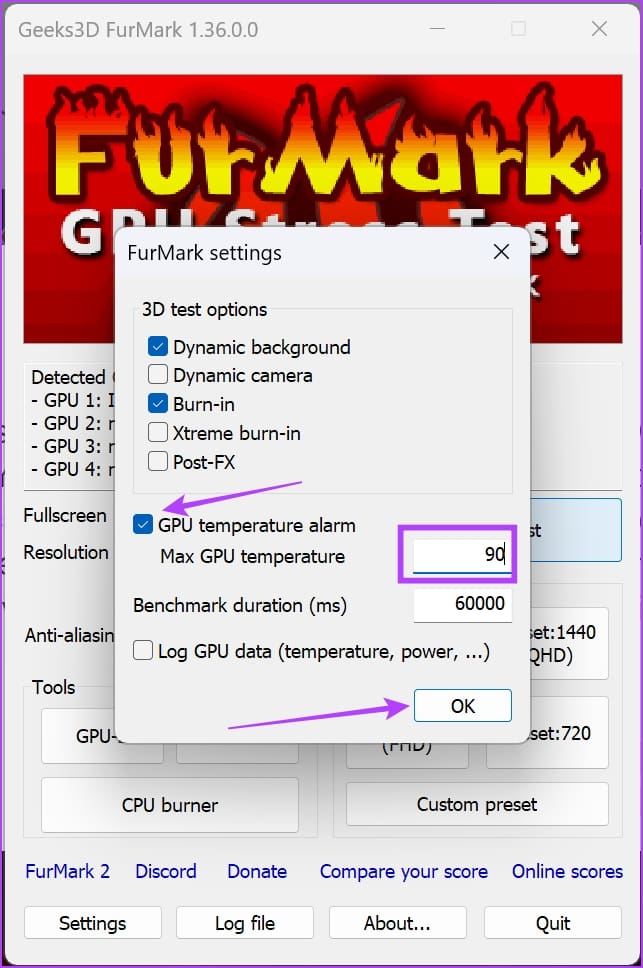
Step 2: Click Settings and set the GPU temperature alarm to 90°C.
Step 3: Click OK to save the temperature alarm.
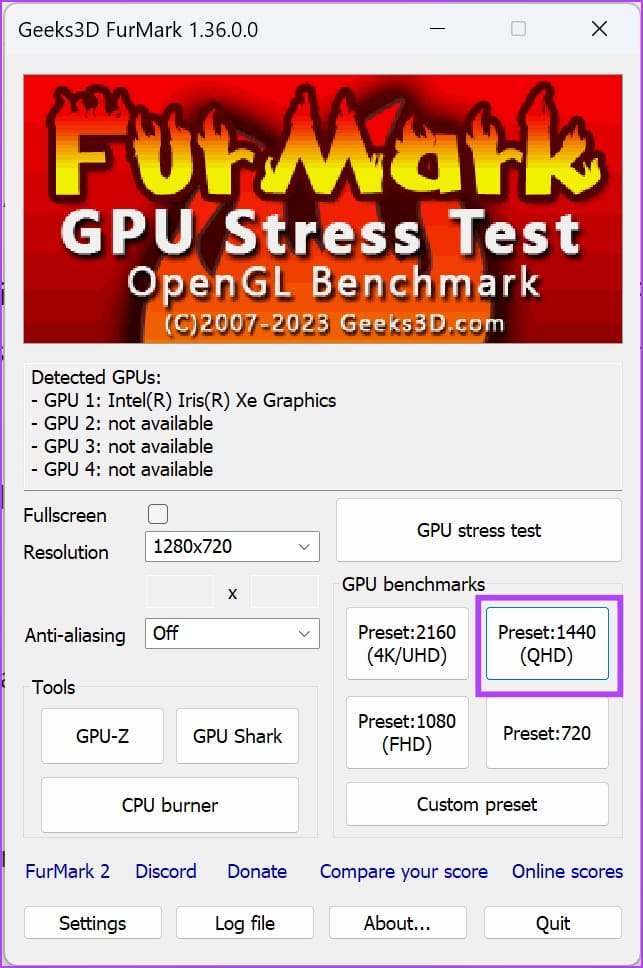
Step 4: Under the GPU Benchmark section, select any preset resolution for benchmarking.
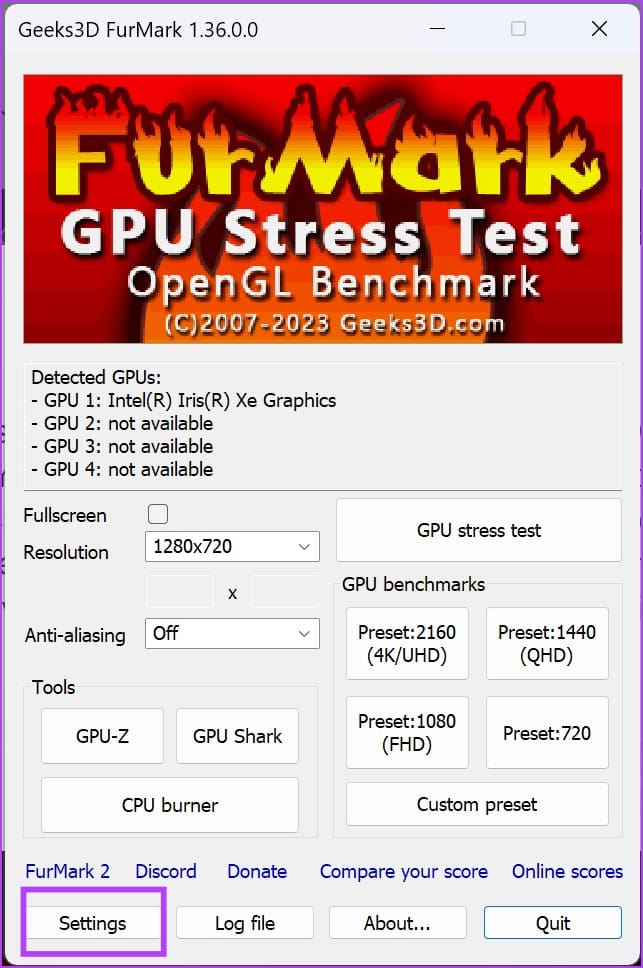
Step 5: On the next screen, click Go.
Step 6: You’ll see a 3D animation for about one minute after you start the GPU benchmarking test. Monitor its performance during the test.
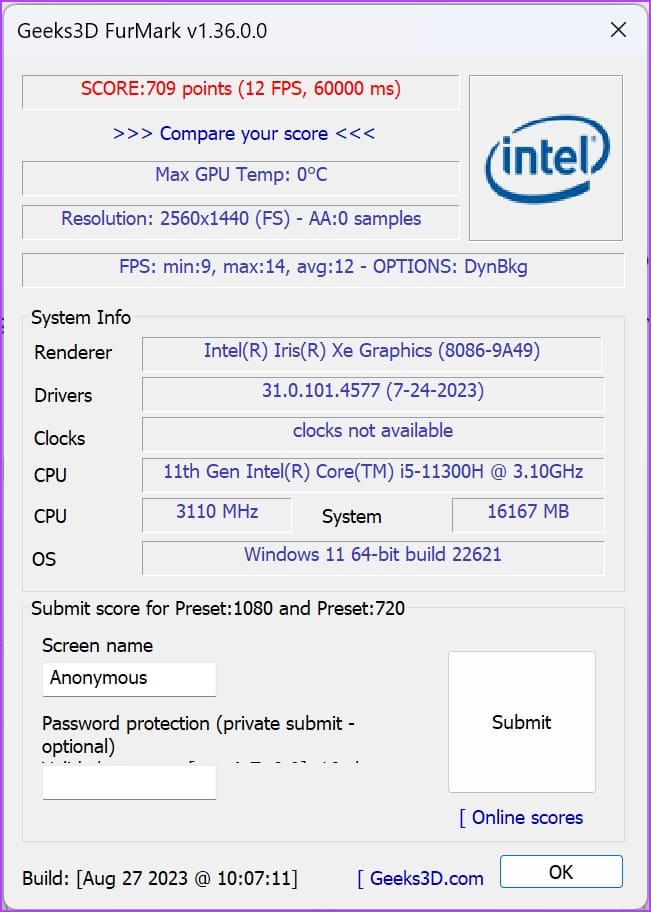
Normally, if you see poor frame per second (FPS) values and higher temperatures for the GPU, its health isn’t good.
At the end of the testing, the tool will generate a score. You can match the score with similar other test results to find a comparative analysis of your GPU health. You’ll find the comparative chart on the FurMark Scores website.
The final method is inspecting the actual hardware by removing the GPU from your computer. You can only do this on your desktop computer. If you’re experiencing GPU issues in your gaming laptop, contact the manufacturer for technical assistance.
It’s a tricky task but important since you’ll know the physical status of the GPU and clean it too. Once you’ve taken out the GPU from your system, look for the following:
- Is the heatsink attached firmly or not
- Cooling fan installed snugly
- Rust or debris on the circuit board
- Thermal paste material coming out in the powdered form






.jpg)


Post a Comment
0 Comments